
I tend to explore what happens to suburbs as they age and begin to decline. But this time I’m going to explore what happens to suburbs that thrive and continue to grow and work their way up the value chain. It isn’t exactly what many people expect. “Be careful what you wish for.”
A friend moved from San Francisco to San Jose this winter. Now that I’ve been visiting her on a regular basis I have an excuse to poke around. It’s actually pretty fascinating.
A friend moved from San Francisco to San Jose this winter. Now that I’ve been visiting her on a regular basis I have an excuse to poke around. It’s actually pretty fascinating. Her tract home was built in 1947 on land that had previously been orchards. By the 1960’s the area had become home to military and aerospace firms that then spun off civilian electronics companies in little low rise office parks. By the 1980’s the area had officially emerged as Silicon Valley. Oracle, Apple, Facebook, Hewlett-Packard, Microsoft, Google, eBay, Juniper Network, PayPal… these companies stretch out for miles in every direction. It’s an economic development dream for local governments. While there are a dozen separate municipalities (Redwood City, Cupertino, Mountain View, Palo Alto, Santa Clara, Fremont, Los Gatos, and so on) the entire southern end of San Francisco Bay is essentially one giant suburban corporate office park blur.
Here are three examples of the kinds of commercial buildings that served earlier waves of businesses in Silicon Valley. They were probably built between the 1970’s and 1990’s. This office park happens to be in the town of Sunnyvale, but nearly identical arrangements can be found all over the Bay Area. In fact, I bet there are buildings just like these in whatever town you live in too whether it’s in Florida, Michigan, or Utah.
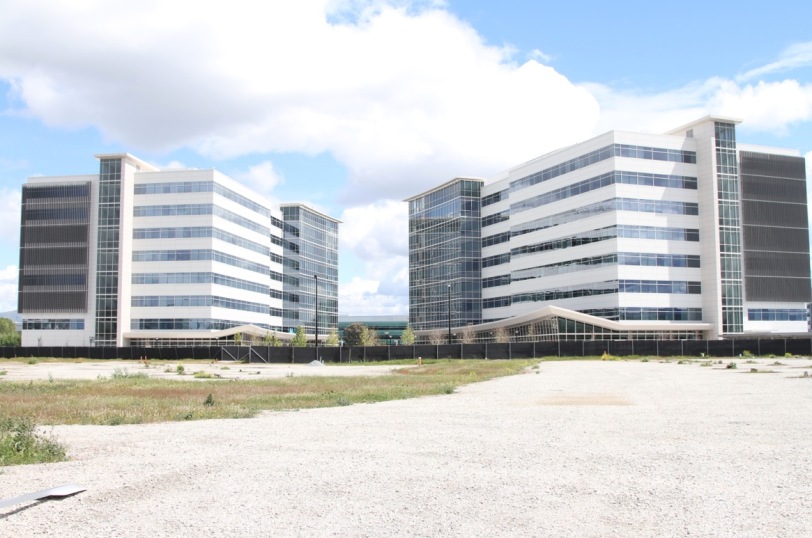
Here’s what’s happening to these office parks as the economy heats up. The land has become very valuable and it makes good economic sense to build new eight or ten story office blocks on vacant land and surface parking lots. It’s good for the tech companies who want to expand their existing operations. It’s good for the land owners who can cash in on the sale. It’s good for the city since it brings increased tax revenue to the municipal coffers. And it’s good for people looking for high paying jobs, both in the initial construction phase and later office workers and support staff. There are, of course, also problems associated with this kind of redevelopment, which I’ll get to in a minute.
Here’s another construction site directly across the street. The old one story buildings were scraped and are being replaced by parking decks and office blocks. These are all part of the same company that is experiencing rapid expansion and doubling their corporate campus that already has over a million square feet of space. These few buildings alone will ultimately house another eight hundred well paid workers. Part of the long term plan for this site is to include a two hundred room hotel for business travelers associated with the company. Perhaps that new hotel will replace the existing one story motel.
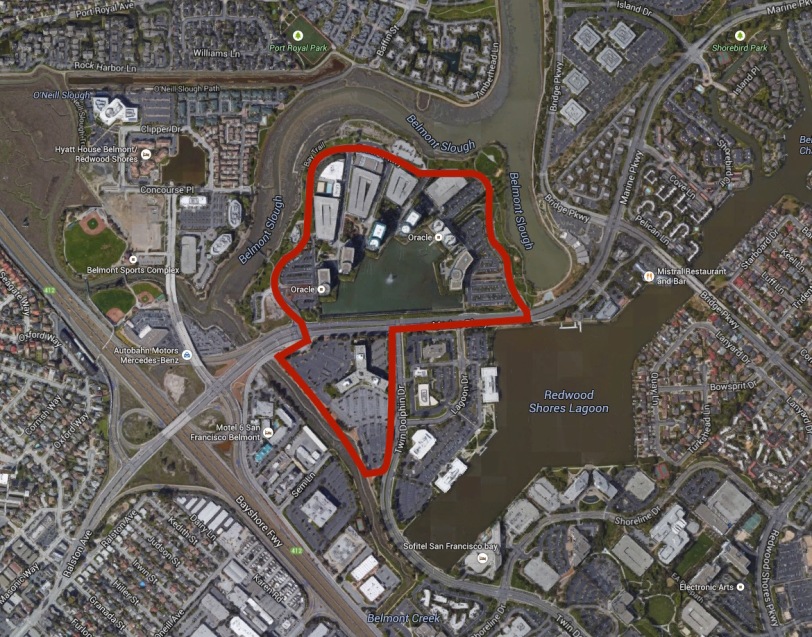
Here’s the bigger picture. Zooming out on Google Earth you can see how multiple older office parks are being absorbed and folded in to much larger more unified corporate complexes. The scale of the construction is too large to capture even with a macro lens on the ground. These tech workers were walking between buildings at lunchtime and it was quite a trek. This kind of land use intensification is actually very similar to how old orchards were converted to residential subdivisions. Land values increased and property was pressed into service for tract homes which were much more lucrative than apricots or prunes. The same process is now unfolding at the next higher economic level with office parks. If I hadn’t taken these photos myself I would swear some of them were computer generated. The buildings have such a generic AutoCAD look about them. And there are dozens of them at this one site alone.
Here’s another corporate campus. This one is in Redwood City. Everywhere you look the old one and two story buildings are being razed and replaced with significantly larger buildings. The schmaltzy motels, strip malls, and office parks of previous decades have been upscaled both physically and economically. This was once open water and marshland that was filled, dredged and contoured in the 1960’s, but has since been redeveloped to a higher value use.
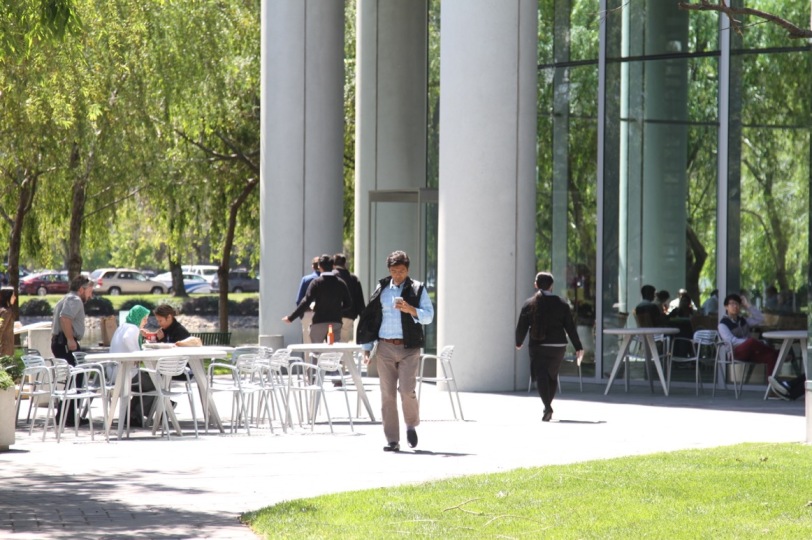
Companies are fond of the “theme park” suburban campus where the environment is akin to an all inclusive resort destination for workers. These are islands – sometime literal islands – in the suburban landscape. From the air these corporate campuses look a lot like Epcot Center at Disney World or a regional shopping mall off the side of a highway.
This inward looking mega block form of development is common in suburbia. The images above show a college, an amusement park, and a corporate office park. When you’re inside one of these bubbles it’s actually very pleasant. But getting to and from these locations is pretty much impossible without a car. Even if you live directly across the street walking wouldn’t work all that well. Add in the fact that many of the nearby residential subdivisions are gated communities and that each of these bubbles are separated by highways, walls, and drainage canals… a car becomes essential. That loads the road network with an insane amount of traffic. If the one story buildings incrementally ramp up to eight story buildings you have a very big transportation problem on your hands.
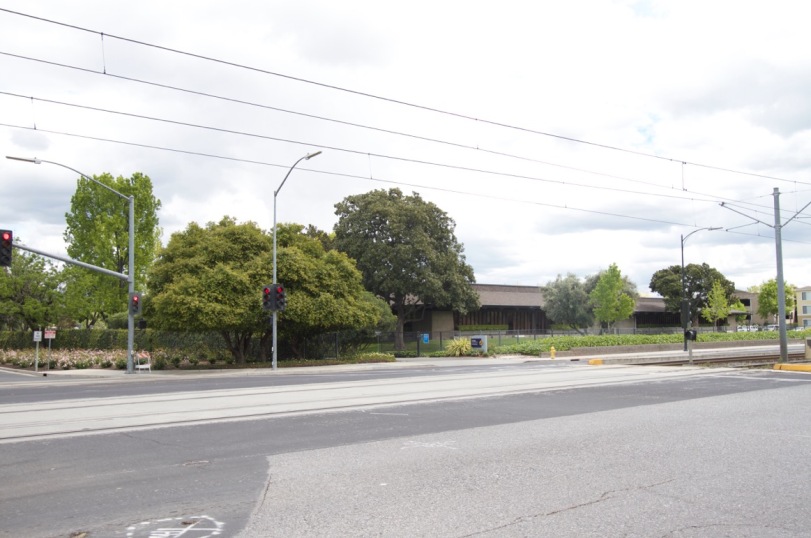
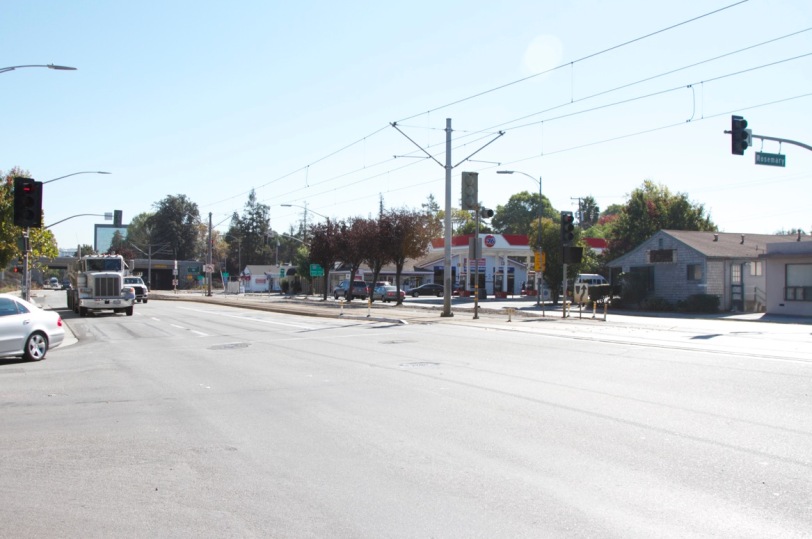
Here’s an intersection halfway between my friend’s house and the corporate campus where she works. It’s a typical suburban commercial corridor lined with standard one story buildings of the office park and light industrial variety that were built anytime from the 1960’s to the 1990’s.
Here’s what’s happening all around Silicon Valley. The small old buildings are being replaced with much larger ones. These aren’t exactly skyscrapers, but they’re significantly more substantial than what was there before.
The same thing is happening with residential property. The old suburban roads lined with gas stations and Kwickie Marts are giving way to multi-story apartment buildings with underground parking decks. These two photos show two sides of the same street. This spot is immediately adjacent to a 1950’s residential subdivision of single family homes. The apartment building fills a need for workforce housing at a high, but tolerable price. One bedroom apartments in this neighborhood rent for about $2,000 a month. Two bedroom units rent for closer to $3,000. If you want to buy an actual house the bargain basement fixer uppers start at $600,000. There are a lot of people in the area who can afford to carry a mortgage of that size, but the problem is often the down payment. Twenty per cent of $600,000 is $120,000. That’s a hurdle many people struggle with. I’ve seen some very nice double wide trailers for sale in the $320,000 range, but that doesn’t include the land under the trailer which you would still need to rent. So rental apartments and condo complexes are in fact necessary in this area if many workers are to live anywhere near where the jobs are.
That brings us to some of the serious problems with an economically successful suburb. Silicon Valley, as the name suggests, is hemmed in by mountains and water. All the flat, easily developed land has already been built on in the standard suburban fashion. Over the decades highways have been built through mountain passes to access new land on the other side of these mountains and many people and businesses have expanded outward to the far edges where possible. But the resulting transportation bottlenecks and commute times are severe. Driving to and from Silicon Valley to the outer outer outer suburbs is like pouring molasses through a funnel. People are willing to pay a lot extra to not have to endure that schlep every day. In theory public transportation could ease the commute for many people, but the dispersed development pattern guaranties that transit will never be efficient or cost effective since most people need to drive from their house to a transit center and then take a shuttle bus to the office at the other end of the train line. Living closer to work is a better option for many people. If you have a million dollars on hand you can buy a nice big home with a front lawn and swimming pool in the back yard. Many people in the area do. The median income in Silicon Valley for people with a bachelor’s degree is $95,000 a year. That’s the median, so half the working population earns more than that. A million dollar house is within reason, particularly if there are two incomes per household to carry the mortgage. If not, living in a condo or apartment complex is the next best option.
From my perspective these intensifying suburbs are in an adolescent phase of development. They are rapidly losing the qualities that people like about the suburbs: open space, privacy, convenience, quiet, lower cost, ample free parking, and so on. But they aren’t yet delivering the things people like about cities: culture, vibrant street life, walkability, convenient public transportation, night life, and such. I stopped and took photos of large numbers of tech workers walking along the side of the eight lane highways at lunchtime. There isn’t anyplace for these folks to walk to. There’s nothing but parking lots, highway fly-overs, gas stations, landscaped berms, and convenience stores as far as the eye can see. When I ask the workers where they’re going they say they’re just stretching their legs and getting some air. They eat lunch (and very often breakfast and dinner) inside their office compounds in subsidized cafeterias. Perhaps in another thirty years the transformation from suburb to something more vital may be complete. Given the suburban chassis these places inherited I don’t see how the underlaying infrastructure will ever support anything other than a bad compromise.
Joel Garreau calls places like this Edge City: a place that has a suburban form but at an urban density. Driving private cars is no longer convenient here anymore, but transit will never function well either. Jobs are plentiful, but housing is too expensive. It lacks the privacy and peace of a good suburb, but is deficient in the vibrancy and culture available in a real city. It’s too thick to be jam, but too thin to be jelly.
John Sanphillippo lives in San Francisco and blogs about urbanism, adaptation, and resilience at granolashotgun.com. He's a member of the Congress for New Urbanism, films videos for faircompanies.com, and is a regular contributor to Strongtowns.org. He earns his living by buying, renovating, and renting undervalued properties in places that have good long term prospects. He is a graduate of Rutgers University.


























































The Fashion Dreams Growth
The fashion is looking the best way to grow in society with new urban culture.he small old buildings are being replaced with much larger ones. These aren’t exactly skyscrapers, but they’re significantly more substantial than what was there before all are best you revealed in new fashion elle. New Fashion Elle