
By Joel Kotkin and Mark Schill
Suburbs may not have cooked up the mortgage crisis, but they absorbed much of initial damage. Now that Wall Street and the big cities are also taking the fall, suburbanites might feel a bit better — but there’s still lots of room for anger out in the land of picket fences, decent schools and shopping malls.
Widely demeaned in the media and academe, suburbs still exercise their power at election time. Home to roughly half the country’s population, and likely a greater share of its voters, suburbs seem destined to remain — to borrow from that great wordsmith George W. Bush — “the decider” in this election.
Indeed, as the campaign has evolved, the critical position of suburbs seems to have grown. Barack Obama’s stranglehold on the urban vote seems unshakeable — even against a maverick “moderate” such as John McCain.
At the same time, after seeming unsettled, the rural and small-town electorate appears to be returning to the GOP fold. Alaska Gov. Sarah Palin’s place on the Republican ticket and, perhaps even more, the mainstream media’s snooty reaction to her, may have sealed the GOP deal in the countryside, at least at the presidential level. One sure sign: The small Obama strike team sent to reliably red North Dakota this summer has departed for more competitive terrain in nearby Minnesota and Wisconsin.
So now it’s really up to the suburbanites, who come from the only geography that has grown faster than the national average over the past 30 years. But it’s critical to recognize that suburbs themselves have changed, becoming more reflective of America’s diversity, just as cities have grown more bifurcated between rich and poor. Once lily white, suburban America is now roughly 21 percent minority.
Voting behavior among suburbs overall also has changed over the years. In the 1980s, Ronald Reagan carried the suburbs in the key swing states by between 20 points and 40 points. Bill Clinton ended this dominance, essentially battling the GOP to a suburban standoff. He even beat the Republicans in the peripheral communities of Pennsylvania, Michigan, Missouri and Florida.
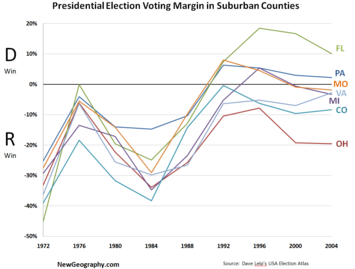 In 2000 and again in 2004, President Bush recovered some of the Republican edge, running as much as 10 percent better than Sen. Bob Dole’s weak 1996 effort. But in the 2006 congressional elections, Democrats regained much of the ground Clinton had carried.
In 2000 and again in 2004, President Bush recovered some of the Republican edge, running as much as 10 percent better than Sen. Bob Dole’s weak 1996 effort. But in the 2006 congressional elections, Democrats regained much of the ground Clinton had carried.
As of now, polls suggest McCain, who lagged in the suburbs into the summer, has pushed back some of the Democratic momentum. He now enjoys, according to the latest Wall Street Journal poll, a 10-point edge among suburban voters, not far from what Bush garnered in those parts of the swing states. If McCain can combine this suburban group with his rural and small-town base, he could be in striking distance of staging an upset.
But this may not be so easy. Democrats’ recent gains seem to be solidifying, particularly in older, metropolitan suburbs. Fairfax County, home to one out of seven Virginians, has been trending strongly Democratic in recent years, even supporting John F. Kerry in 2004.
McCain, who appeals more to independents than Bush did, should be able to erode some of this advantage in such communities. But Palin’s social conservatism could turn off many generally well-educated, middle-of-the-road voters who are so prominent in many of the most upscale suburban communities.
At the same time, Palin — herself a former mayor of an Anchorage exurb — could help McCain consolidate Bush’s gains in the fast-growing exurbs, which tend to be more heavily composed of traditional families and generally less ethnically diverse. In his 2004 victory, Bush won 97 of the nation’s 100 fastest-growing counties with roughly 63 percent of the vote. If McCain can duplicate that feat, he will be well-positioned.
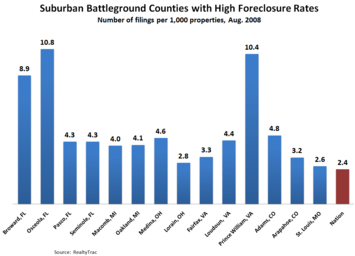 Several factors, notably the financial crisis, could work against these efforts. Foreclosure rates in many of these exurban suburban counties are well above the national average, particularly in Florida and the Virginia suburbs of Washington and also outside Denver, Detroit and Cleveland.
Several factors, notably the financial crisis, could work against these efforts. Foreclosure rates in many of these exurban suburban counties are well above the national average, particularly in Florida and the Virginia suburbs of Washington and also outside Denver, Detroit and Cleveland.
The mortgage crisis affects not only foreclosed homeowners, but also homeowners who are still above water. First, foreclosures lower everybody’s home values and bring on the possibility of renters replacing owners — not a good development in a suburban context. Second, particularly in exurban counties, construction has often been the basis for a lot of job growth in this decade, because construction jobs and other employment related to the real estate industry has been centered there.
All of this makes suburbs a theoretically good target for Obama. In places like Pennsylvania, as longtime Republican activist Dennis Powell suggests, Obama should try to duplicate Democratic Gov. Ed Rendell’s wildly successful performance in 2002 in the so-called collar counties around Philadelphia. By winning those counties, in addition to building up a huge margin in his native Philadelphia, Rendell built a margin of more than a half-million votes that helped him win, even while he was getting thrashed throughout most of the rest of the state.
In 2004, Kerry also won Pennsylvania’s collar counties, not by a large margin but by enough to secure his victory in the state. If Obama does as well as Kerry in the collar counties, he will win the state — perhaps not at a Rendellian scale, but comfortably enough.
For his part, McCain needs to emulate the success of maverick Republicans, such as Sen. Arlen Specter, who have won by winning the Philadelphia suburbs. If McCain can replicate Specter’s performance and add some of the disgruntled Clinton Democrats in the rural south and west of the state, he could pull off a game-changing upset.
McCain also has an opportunity to win in the Detroit suburbs, where Obama’s ties to disgraced former Detroit Mayor Kwame Kilpatrick could hurt him. Bush won those areas in 2000 and 2004, but not by enough to capture the state’s electoral votes. As in Pennsylvania, McCain needs to forge a rural-suburban coalition to capture this traditionally blue-tinged state.
For Obama, suburbs in wobbly red states such as Ohio, Florida, Colorado, Virginia and Missouri offer similarly critical opportunities. Even traditionally conservative exurban voters may feel that under Bush they have been led down the bubble path only to have it pop painfully in their faces.
Ultimately it may all come down to “body language.” In our estimation, Obama’s weakness stems not so much from his race — he may well run better in suburbia than did the very white Kerry — but with his close identification with Chicago and Mayor Richard Daley’s Democratic machine. Having spent his adulthood in college towns and big cities, Obama seems to lack the instinctive Clintonian understanding of the suburban mindset. You never got the sense that Clinton was too urbane to wolf down a Big Mac or get a Slurpee at the local strip mall — and he really seemed to “feel the pain” of an overstressed homeowner.
In contrast, Obama and his team, including campaign manager David Axelrod, reflect the mentality of a totally urban political culture. Obama’s intellectual and media supporters also include elements — ensconced at publications such as The New York Times and The Atlantic Monthly as well as within the leftist Netroots — that often regard suburbs and their denizens as a form of social and environmental pestilence.
Obama is simply too smart, as a candidate and perhaps also as a president, to publicly give in to this mindset. He’s certainly trying to appeal to suburban voters who are too concerned with issues such as health care and foreclosures to worry about his lack of geographic empathy.
If he can convey this message effectively, Obama could benefit from the suffering now taking place in suburban communities. There may well be enough disgruntled suburban voters, even in the more peripheral areas, to blunt McCain’s suburban lead down to manageable numbers.
If so, McCain’s rural and small town base will not be enough to win the critical swing states and the election. If the Republicans can hold their 2004 suburban base, though, McCain could yet triumph. Whatever the result, one thing is clear: Suburban voters will be the deciders.
Joel Kotkin is a presidential fellow at Chapman University and executive editor of www.newgeography.com. Mark Schill is a principal at Praxis Strategy Group and the site’s managing editor.












