
Lately, Texas has been noted frequently for its superior economic performance. The most recent example is the CNBC ratings, which designated the Lone Star state as the top state for business in the nation. Moreover, Texas performed far better than its principal competitor states during the Great Recession as is indicated in our How Texas Averted the Great Recession report, authored for Houstonians for Responsible Growth.
Introduction: How Texas averted the Great Recession:
One reason that Texas did so well is that it fully escaped the “housing bubble” that did so much damage in California, Florida, Arizona, Nevada and other states. One key factor was the state’s liberal, market oriented land use policies. This served to help keep the price of land low while profligate lending increased demand. More importantly, still sufficient new housing was built, and affordably. By contrast, places with highly restrictive land use policies (California, Florida and other places, saw prices rise to unprecedented heights), making it impossible for builders to supply sufficient new housing at affordable prices (overall, median house prices have been 3.0 times or less median household incomes where there are liberal land use policies).
The Great Recession: The world-wide Great Recession was the deepest economic decline since the Great Depression: This downturn hit average households very hard. According to Federal Reserve Board "flow of funds" data, gross housing values declined 9 quarters in a row through the first quarter of 2009. The previous modern record is a single quarter. From the peak to the trough, household net worth was reduced a quarter, which is more than 1.5 times the previous record decline.
Texas Largely Avoided the Great Recession. Texas has largely escaped the economic distress experienced around the nation, and especially that of its principal competitors, California and Florida. By virtually all measures, Texas has performed better in growth of gross domestic product, employment, unemployment, personal income, state tax collections, and consumer spending This is in part due to much less mortgage distress in Texas. At the bottom of the economic trough, the Brookings Institution Metropolitan Monitor ranked the performance of the 6 largest Texas metropolitan areas among the top 10 in the nation. The latest Metropolitan Monitor ranked each of the 6 metropolitan areas in the highest performance category.
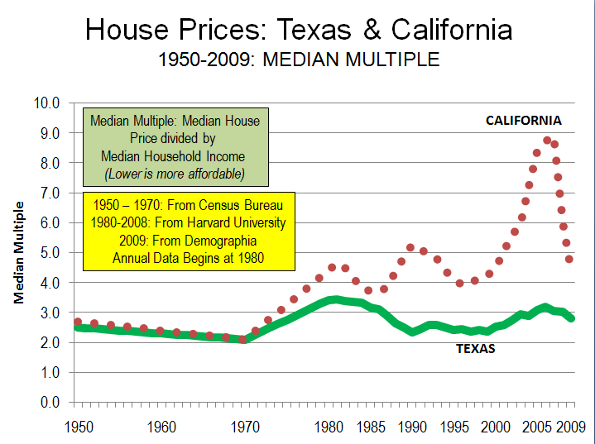
Throughout the past decade, Texas has experienced far smaller house price increases than in California, Florida and many other states. During the bubble, California house prices increased at a rate 16 times those of Texas, while Florida house prices increased 7 times those of Texas. As a result, after the bubble burst, subsequent house price declines were far less severe or even non-existent in Texas. Texas had experienced its own housing bubble in the 1980s, however even then overall prices did not exceed the Median Multiple of 3.0 (The Median Multiple is the median house price divided by the median household income).
Unlike Texas, all of the markets with steep house price escalation had more restrictive land use regulations. This association between more restrictive use regulation and higher house prices has been noted by a wide range economists, from left-leaning Nobel Laureate Paul Krugman to the conservative Hoover Institution’s Thomas Sowell. It is even conceded in The Costs of Sprawl ---2000, the leading academic advocacy piece on more restrictive land use controls, which indicates the potential for higher house or land prices in 7 of its 10 recommended strategies.
Comparing Texas and California: Unlike California, housing remained affordable in Texas. California’s housing affordability - in relation to income – largely tracked that of Texas (and the nation) until the early 1970s (Figure). After more restrictive land use regulations were adopted prices started to escalate. This relationship has been well demonstrated by William Fischel of Dartmouth University. Other factors have had little impact. Construction cost increases have been near the national average in California. Other factors, like underlying demand as measured by domestic migration, have been lower in California than in Texas..
Comparing Texas and Florida: The contrast with Florida is similar. Housing affordability in Florida was comparable to that of Texas as late as the 1990s. However, with strict planning control of land for development in Florida, land prices rose substantially when profligate lending increased demand.
Comparing Texas and Portland: Further, the Texas housing market avoided the huge price increases that have occurred in Portland (Oregon), which relies on extensive restrictive land use regulation. In 1990, Portland house prices relative to incomes were similar to those of the large Texas metropolitan areas. At the recent peak, the median Portland house price soared to approximately 80% above Texas prices. Portland did not experience the price collapses of California, but due to the greater price volatility associated with smart growth price declines in relation to incomes that were five times those of Texas.
How the Speculators Missed Texas: Speculation is often blamed as having contributed to the higher house prices that developed in California and Florida. This is correct. Moreover, with some of the strongest demand in the United States, Texas would seem to have been a candidate for rampant speculation. After all, it happened back in the 1970s when a huge oversupply of housing, industrial, retail and office space collapsed in the face of falling energy prices.
But it did not happen this time, despite solid population growth. During the housing bubble, Dallas-Fort Worth and Houston ranked second and third to Atlanta in population increases among metropolitan areas with more than 5 million population. Austin is the nation’s second fastest growing metropolitan area with more than 1 million population. Each of these metropolitan areas had strong underlying demand, as indicated by domestic migration data.
Yet the speculators were not drawn to the metropolitan areas of Texas. This is because speculators or "flippers" are not drawn by plenty, but by perceived scarcity. In housing, a sure road to scarcity is to limit the supply of buildable land by outlawing development on much that might otherwise be available.
However, the speculators did not miss California and Florida. Nor did they miss Las Vegas or Phoenix, where the price of land for new housing rose between five and 10 times as the housing bubble developed. Despite their near limitless expanse of land, much of it was off limits to building, and the exorbitant price increases were thus to be expected.
The Threat: Yet, despite the success of the less restrictive land use policies in Texas, there are strong efforts there to impose more smart growth policies. The impact could be devastating, especially from strategies that ration land that would raise land and house prices, as has occurred in California and Florida. In 2009, Governor Perry vetoed a bill that would have required the state to promote smart growth. Federal initiatives, under proposed climate change and transportation acts could do much to destroy not only the affordability of Texas metropolitan markets, but could also make Texas less competitive in the decades ahead.
Photograph: Suburban San Antonio (by the author)
Wendell Cox is a Visiting Professor, Conservatoire National des Arts et Metiers, Paris. He was born in Los Angeles and was appointed to three terms on the Los Angeles County Transportation Commission by Mayor Tom Bradley. He is the author of "War on the Dream: How Anti-Sprawl Policy Threatens the Quality of Life.”













What does a Marriott Trip
What does a Marriott Trip Club villa need to give? Here's a typical situation - accommodations for 6 to eight individuals - about one,one hundred square feet - with separate dwelling and dining region and many bathrooms. marriott
emoney
with pleurisy brought on by cirrhosis of the liver. He was moved to the St Joseph Hospital and was given a private room paid for by the fabulously wealthy Comte de Beaumont. It was there that he died in 1925. It is hard to sum up any life in a single line, emoney
Thomson Three
That is very interesting Smile I love reading and I am always searching for informative information like this. This is exactly what I was looking for. Thanks for sharing this great article Thomson Three
Nice knowledge gaining
Nice knowledge gaining article. This post is really the best on this valuable topic.
Master Tone Pickups Tips And Tricks
Many people do not realize
Many people do not realize they are able pay significantly less for a house than what is being asked. All you have to do is learn how to haggle. This does not mean arguing with the seller of the house. Rather, use specific strategies to obtain the house for the price that you want. Thank you.
Glendale AZ Realtors
Awsome post
sandhi sudha plus
nice post
Yes I would say that we were
Yes I would say that we were very lucky when it came to the recession, it definitely could have been a lot worse! However I did notice that our homes didn't seem to fair much better than the rest of the economy's. Killeen real estate certainly saw some homes go up on the market over the last couple years.
Important Question - Why no Texas real estate boom & bust?
A great question because if we can figure out what Texas did right, other states may be able take the same actions to avoid real estate booms and busts in the future. States would be able to control of their own destiny without hoping Washington will solve their problem.
I don't know the solution, but here are some thoughts.
1) Restrictive land use policies were a factor but not as important to my mind as in the author's. For example, in Arizona where I'm from, land use restrictions weren't a huge constraint to new housing development.
However, skyrocketing home builder prices in Arizona, although rational, created a price umbrella under which every homeowner on the periphery could raise their prices with impunity. In addition, Arizona home builders continued overbuilding long after the music stopped which greatly exacerbated the housing bust.
2) Texas banking regs. A Washington Post writer mentioned as a key factor that Texas has an 80% maximum loan-to-value limit for home mortgage refinancing and home equity lines of credit. So the 80% loan-to-value limit, to a degree, protects responsible homeowners from the effects of those less responsible homeowners who would have ended up in foreclosure if they had done a larger cash out refi.
A large part of the current crisis was caused by people who had tons of equity, doing cash out refis near the top and then eventually when prices fell losing their homes and driving down their neighbors' home prices.
Further, since cash out refis were such a common way for Joe Investor to get the down payment for his investment property, the 80% rule would have thwarted many of those novice investment purchases that helped stoke home prices. Working a couple of different ways, the 80% rule would have prevented many home owners from losing their homes.
I assume there are other Texas banking regulations that had an impact and I would love to hear about them.
3) Texas property taxes. I wouldn't want Arizona to copy this mechanism but property taxes are so incredibly high in Texas that it makes it harder to make money speculating on real estate. If you don't flip that home quickly, the property taxes can eat you up. The high property taxes discourage speculators. (California property taxes are a significant factor in restricting housing supply in my opinion but that's another story.)
4) Texas is far from California. The boom from the Arizona point of view, started in California, spread to Las Vegas and then to Arizona. The boom was in the process of spreading to Texas and Utah when it petered out.
The boom was caused by people, not just economics. As a Realtor in Arizona, the vast majority of investors I spoke with were Californians and some Nevadans. They had made a ton of money earlier in California and Nevada booms so they had the money and the motivation to do it again in nearby markets that hadn't taken off yet. As Phoenix boomed they started looking to Texas and Utah for new cheaper markets to conquer.
5) The internet. In the olden days, it would take a California real estate investor a ton of work to learn about the Arizona real estate market. They might spend a few days in Phoenix on a few different trips before they bought an investment home.
The internet changed everything. California investors would study the real estate market online and even select the homes they wanted to see before they ever came to Arizona. Then they would drive to Arizona and make an offer on a home within a couple of days.
Anyway, this is a fascinating subject. I would love to hear why you think Texas dodged the bullet this time.
housing prices in texas
While I don't dispute that difference in land use regulation between Texas and the other places mentioned has an effect, I think you are overlooking a more basic factor in play here. There are severe restrictions on mortgage loans that banks can make in this state, according to a banking law expert I have talked to. If prospective buyers cannot get loans for over-priced houses, then no drastic price inflation can take place, unless of course the buyers are in a position to pay out of their own savings. Thus, even though Austin has many of the same kinds of land use restrictions as the other markets you cite (particularly for building in what is perceived to be the environmentally sensitive hills to the west), its prices are only slightly higher than those in Houston, Dallas and San Antonio, and have never soared to any of the kinds of levels seen in the bubble states. I am guessing that these restrictions on mortgage loans have been put in place since the great real estate boom and bust of the 1980s, when S&L money was being lent lavishly (and even though the land use restrictions were no more restrictive than today).
That's actually an
That's actually an interesting point and one I hadn't heard of before. I had wondered why prices in some parts of Texas didn't go absolutely nuts like in other places- in particular Austin. Having loan restrictions would make bubble inflation more difficult. I wish the same restrictions had been in place in Cali where stories of strawberry pickers buying $700,000 houses were shockingly common.